11 March 2025
Oliver Smith
BY EMAIL: xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx@xxxxxxxxxxx.xxx.xx
In reply please quote:
FOI Request:
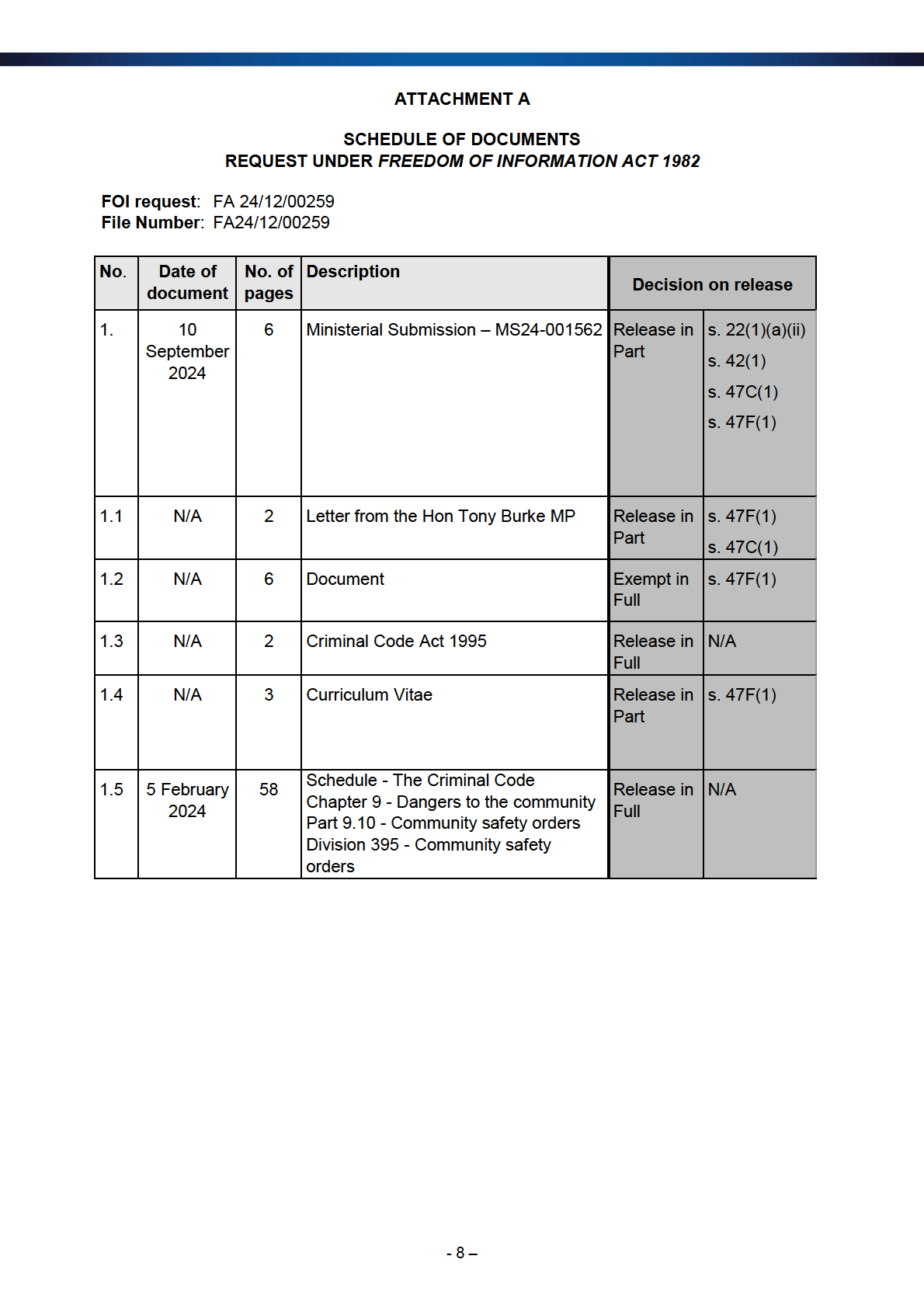
FA 24/12/00259
File Number:
FA24/12/00259
Dear Oliver Smith,
Freedom of Information (FOI) request – Decision
On 4 December 2024, the Department of Home Affairs (the Department) received a request for
access to documents under the
Freedom of Information Act 1982 (the FOI Act).
The purpose of this letter is to provide you with a decision on your request for access under the
FOI Act.
1
Scope of request
You have requested access to the following documents:
Under the FOI Act, I seek a copy of the Ministerial Brief provided to the office of Home
Affairs Minister Tony Burke on 10/9/24 with the Brief PDR No. MS24-001562.
2
Authority to make decision
I am an officer authorised under section 23 of the FOI Act to make decisions in respect of
requests to access documents or to amend or annotate records.
3
Relevant material
In reaching my decision I referred to the following:
• the terms of your request
• the documents relevant to the request
• the FOI Act
• Guidelines published by the Office of the Information Commissioner under section 93A
of the FOI Act (the FOI Guidelines)
• advice from Departmental officers with responsibility for matters relating to the
documents to which you sought access
PO Box 25 Belconnen ACT 2616
• xxx@xxxxxxxxxxx.xxx.xx • www.homeaffairs.gov.au
 4
Documents in scope of request
4
Documents in scope of request
The Department has identified six documents as falling within the scope of your request. These
documents were in the possession of the Department on 4 December 2024 when your request
was received.
Attachment A is a schedule which describes the relevant documents and sets out my decision
in relation to each of them.
5
Decision
The decision in relation to the documents in the possession of the Department which fall within
the scope of your request is as follows:
• Release two documents in full
• Release three documents in part with deletions
• Exempt one document in full from disclosure
6
Reasons for Decision
My findings of fact and reasons for deciding that the exemption provision applies to that
information are set out below.
6.1 Section 42 of the FOI Act – Legal Professional Privilege
Section 42 of the FOI Act provides that a document is an exempt document if it is of such a nature
that it would be privileged from production in legal proceedings on the ground of legal professional
privilege.
I am satisfied that parts of Document 1 comprise confidential communication passing between
the Department and its legal advisers, for the dominant purpose of giving or receiving legal
advice.
In determining that the communication is privileged, I have taken into consideration the following:
• there is a legal adviser-client relationship
• the communication was for the purpose of giving and/or receiving legal advice;
• the advice given was independent and
• the advice was given on a legal-in-confidence basis and was therefore confidential.
The content of these documents are not part of the rules, guidelines, practices or precedents
relating to the decisions and recommendations of the Department. The documents do not fall
within the definition of operational information and remain subject to legal professional privilege.
I have decided that parts of Document 1 are exempt from disclosure under section 42 of the FOI
Act.
6.2 Section 47C of the FOI Act – Deliberative Processes
Section 47C of the FOI Act provides that a document is conditionally exempt if its disclosure
would disclose deliberative matter relating to the deliberative processes involved in the functions
of the Department.
- 2 –
link to page 3 link to page 3 link to page 3

‘
Deliberative matter’ includes opinion, advice or recommendation obtained, prepared or
recorded, or consultation or deliberation that has taken place, in the deliberative processes of an
agency.
‘
Deliberative processes’ generally involves “
the process of weighing up or evaluating competing
arguments or considerations”
1 and the ‘
thinking processes –the process of reflection, for
example, upon the wisdom and expediency of a proposal, a particular decision or a course of
action.’
2
The document contains advice, opinions and recommendations prepared or recorded in the
course of, or for the purposes of, the deliberative processes involved in the functions of
Department. I am satisfied that this deliberative matter relates to a process that was undertaken
within government to consider whether and how to make or implement a decision, revise or
prepare a policy, administer or review a program, or some similar activity.
3
Disclosure of this deliberative information could reasonably be expected to inhibit full and frank
advice from the Department to its Minister, and, as a result, full consideration by the Government
on any potential future consideration of amendments to legislation.
Section 47C(2) provides that “deliberative matter” does not include purely factual material. I am
satisfied that the deliberative material is not purely factual in nature.
I am further satisfied that the factors set out in subsection (3) do not apply in this instance.
I have decided that the information is conditionally exempt under section 47C of the FOI Act.
Access to a conditionally exempt document must generally be given unless it would be contrary
to the public interest to do so. I have turned my mind to whether disclosure of the information
would be contrary to the public interest, and have included my reasoning in that regard in
paragraph 6.4 below.
6.3 Section 47F of the FOI Act – Personal Privacy
Section 47F of the FOI Act provides that a document is conditionally exempt if its disclosure
under the FOI Act would involve the unreasonable disclosure of personal information of any
person. ‘Personal information’ means information or an opinion about an identified individual, or
an individual who is reasonably identifiable, whether the information or opinion is true or not, and
whether the information or opinion is recorded in a material form or not (see section 4 of the FOI
Act and section 6 of the
Privacy Act 1988).
I consider that disclosure of the information marked
's. 47F(1)' in the documents would disclose
personal information relating to third parties. The information within the documents would
reasonably identify a person, either through names, positions or descriptions of their role or
employment circumstance.
1
Dreyfus and Secretary Attorney-General’s Department (Freedom of information) [2015] AATA 962 [18]
2
JE Waterford and Department of Treasury (No 2) [1984] AATA 67
3
Dreyfus and Secretary Attorney-General’s Department (Freedom of information) [2015] AATA 962
- 3 –

The FOI Act states that, when deciding whether the disclosure of the personal information would
be ‘unreasonable’, I must have regard to the fol owing four factors set out in s.47F(2) of the
FOI Act:
•
the extent to which the information is well known;
•
whether the person to whom the information relates is known to be (or to have been)
associated with the matters dealt with in the document;
•
the availability of the information from publicly available resources;
•
any other matters that I consider relevant.
I have considered each of these factors below.
The information relating to the third parties is not well known and would only be known to a limited
group of people with a business need to know. As this information is only known to a limited
group of people, the individuals concerned are not generally known to be associated with the
matters discussed in the document. This information is not available from publicly accessible
sources.
I do not consider that the information relating specifically to the third parties would be relevant to
the broader scope of your request, as you are seeking access to a Ministerial Brief rather than
information which wholly relates to other individuals.
I am satisfied that the disclosure of the information within the documents would involve an
unreasonable disclosure of personal information about a number of individuals.
I have decided that the information referred to above is conditionally exempt under section 47F
of the FOI Act. Access to a conditionally exempt document must generally be given unless it
would be contrary to the public interest to do so. I have turned my mind to whether disclosure of
the information would be contrary to the public interest, and have included my reasoning in that
regard below.
6.4 The public interest – section 11A of the FOI Act
As I have decided that parts of the documents are conditionally exempt, I am now required to
consider whether access to the conditionally exempt information would be contrary to the public
interest (section 11A of the FOI Act).
A part of a document which is conditionally exempt must also meet the public interest test in
section 11A(5) before an exemption may be claimed in respect of that part.
In summary, the test is whether access to the conditionally exempt part of the document would
be, on balance, contrary to the public interest.
In applying this test, I have noted the objects of the FOI Act and the importance of the other
factors listed in section 11B(3) of the FOI Act, being whether access to the document would do
any of the following:
(a)
promote the objects of this Act (including all the matters set out in sections 3 and
3A)
(b)
inform debate on a matter of public importance
(c)
promote effective oversight of public expenditure
(d)
allow a person to access his or her own personal information.
- 4 –

Having regard to the above I am satisfied that:
•
Access to the documents would promote the objects of the FOI Act.
•
The subject matter of the documents may have a general characteristic of public
importance.
•
No insights into public expenditure wil be provided through examination of the
documents.
•
You do not require access to the documents in order to access your own personal
information.
I have also considered the following factors that weigh against the release of the conditionally
exempt information in the documents:
•
A Ministerial Submission plays an important role in the relationship between a
Department and its Minister. Its purpose is to provide frank and honest advice. It is
inherently confidential between the Department and its Minister and the preparation
of a Ministerial Submission is essentially intended for the audience of that Minister
alone. A precedent of public disclosure of advice given as a part of a Ministerial
Submission would result in:
o
concerns existing in the open and honest nature of advice being provided which
may then hinder future deliberations and decision making processes for the
Department and the Government as a whole and
o
future Ministerial Submissions being prepared with a different audience in mind,
which would compromise the quality of the advice being prepared for the
Minister.
•
I consider that the public interest in protecting the process of the provision of free and
honest confidential advice by a Department to its Minister has, on balance, more
weight, than the public interest that might exist in disclosing the deliberative matter.
Endangering the proper working relationship that a Department has with its Minster
and its ability to provide its Minister with honest advice confidentially would be
contrary to the public interest.
•
Disclosure of personal information which is conditionally exempt under section 47F
of the FOI Act could reasonably be expected to prejudice the protection of third
parties’ right to privacy. It is firmly in the public interest that the Department uphold
the rights of individuals to their own privacy, and this factor weighs strongly against
disclosure.
•
I am satisfied that if the Department were to release personal information without that
person’s express consent to do so, it would seriously undermine public confidence in
the Department’s ability to receive, retain and manage personal information. I
consider such a loss of confidence to be against the public interest, and this factor
weighs strongly against disclosure.
- 5 –

I have also had regard to section 11B(4) which sets out the factors which are irrelevant to my
decision, which are:
a)
access to the document could result in embarrassment to the Commonwealth
Government, or cause a loss of confidence in the Commonwealth Government
b)
access to the document could result in any person misinterpreting or
misunderstanding the document
c)
the author of the document was (or is) of high seniority in the agency to which the
request for access to the document was made
d)
access to the document could result in confusion or unnecessary debate.
I have not taken into account any of those factors in this decision.
Upon balancing all of the above relevant public interest considerations, I have concluded that the
disclosure of the conditionally exempt information in the documents would be contrary to the
public interest and it is therefore exempt from disclosure under the FOI Act.
7
Legislation
A copy of the FOI Act is available at https://www.legislation.gov.au/Series/C2004A02562. If you
are unable to access the legislation through this website, please contact our office for a copy.
8
Your review rights
Internal Review
You do not have the right to seek an internal review of this decision. This is because section
54E(b) of the FOI Act provides that, when an agency is deemed to have refused an FOI request
under section 15AC of the FOI Act, the applicant does not have the right to seek an internal
review of the deemed decision.
The Department was deemed to have refused your request under section 15AC of the FOI Act
because it did not make this decision within the statutory timeframes for the request.
While the Department has now made a substantive decision on your request, section 15AC of
the FOI Act continues to apply to your request, which means that any request you make for
internal review wil be invalid.
Information Commissioner Review
You can instead request the Australian Information Commissioner to review this decision. If you
want to request an Information Commissioner review, you must make your request to the Office
of the Australian Information Commissioner (OAIC) within 60 days of being notified of this
decision.
You can apply for an Information Commissioner review at:
Information Commissioner review
application form on the OAIC website.
- 6 –

If you have already applied for an Information Commissioner review, there is no need to make a
new review request. The OAIC wil contact you shortly to give you an opportunity to advise
whether you wish the review to continue, and to provide your reasons for continuing the review.
You can find more information about Information Commissioner reviews
on the OAIC website.
9
Making a complaint
You may make a complaint to the Australian Information Commissioner if you have concerns
about how the Department has handled your request under the FOI Act. This is a separate
process to the process of requesting a review of the decision as indicated above.
You can make an FOI complaint to the Office of the Australian Information Commissioner
(OAIC) at:
FOI Complaint Form on the OAIC website.
10 Contacting the FOI Section
Should you wish to discuss this decision, please do not hesitate to contact the FOI Section at
xxx@xxxxxxxxxxx.xxx.xx.
Yours sincerely,
[Electronically signed]
Josefina
Position No. 60182600
Authorised Decision Maker
Department of Home Affairs
- 7 –